Bleeding Gums
My gums bleed, and they look red and swollen.
Red, swollen and bleeding gums may be a sign of gum disease. It is most commonly caused by buildup of plaque at the gumline.
You can start by practicing good oral hygiene and removing plaque through proper tooth brushing and interdental cleaning. You should also schedule a visit to your dentist to assess the condition and receive early treatment, if necessary, to reverse this mild condition.
Read on to find out more.

WHAT IS THE PROBLEM?
Redness, swelling, and bleeding are all signs of gum disease – most commonly caused by dental plaque. Where the gum surrounds the tooth, the tissue should look pale pink and should not look puffy or swollen
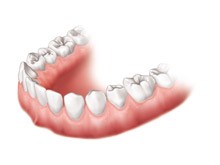 Figure: Healthy gums
Figure: Healthy gums 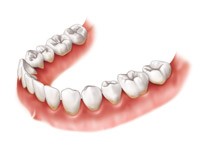 Figure: Red and swollen gums
Figure: Red and swollen gumsHOW IS BLEEDING GUMS OR SWOLLEN GUMS CAUSED?
Dental plaque is a bio film of bacteria that grows all around our mouths and generally does not cause harm. Around the teeth and gums it may cause harm if it is not removed daily. As the dental plaque grows, the bacteria multiply and become harmful. The by-products of the bacteria cause the tissue to become inflamed (red and swollen in appearance). Inflamed tissues bleed easily, and inflamed gums bleed when brushed, even gently. Dental plaque is soft, so it is easily removed with a gentle but thorough brushing action.
WHAT ARE THE WARNING SIGNS TO AVOID BLEEDING GUMS?
There are no warning signs of gum disease before it starts! A little infrequent bleeding when cleaning teeth is an early sign of a gum disease. Most commonly this is not so serious and is a condition known as gingivitis. Thorough daily plaque removal, together with a professional cleaning, will reverse this mild condition. With careful daily oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups, the problem should not return. However, if the bleeding gums and swelling gums are frequent and continue, you may have a more serious condition where the gum and the bone holding the tooth into the jaw suffer permanent damage. This is periodontitis and will need treatment from a dentist or dental hygienist as well as improved plaque removal on your own. The signs and symptoms of both gingivitis and periodontitis are very similar; only a dental check-up can detect the difference.
HERE’S REMEDIES TO PREVENT BLEEDING GUMS:
All teeth and gums: To avoid bleeding gums or swollen gums, brush all teeth and gums thoroughly with a good quality toothbrush designed to reach into and help clean all the difficult-to-reach areas. It is here that the dental plaque builds-up – especially along the gum margin, under the gums, and between the teeth.
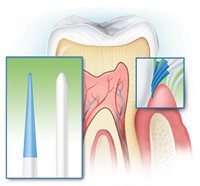 Figure: Toothbrushes with extremely tapered bristles can reach further under the gum and between the teeth in the hard-to-reach areas than regular “end-rounded” bristles.
Figure: Toothbrushes with extremely tapered bristles can reach further under the gum and between the teeth in the hard-to-reach areas than regular “end-rounded” bristles.Hold the brush so the bristles are pointing towards the gum margin at 45 degrees to the tooth roots and brush with short back and forth vibrating strokes, making sure all the surfaces and sides of all teeth get brushed equally. This should take about two minutes to do well. Check with your dental hygienist for the technique that suits your mouth best.
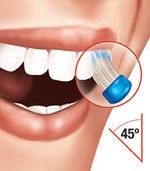 Figure: A key feature of the Bass Technique is placing the bristles at a 45-degree angle to the tooth.
Figure: A key feature of the Bass Technique is placing the bristles at a 45-degree angle to the tooth.Between the teeth: Toothbrushes are not able to clean perfectly in the hard-to-reach areas between the teeth – a place where bleeding often occurs and gum disease starts. Each day use an interdental brush or dental floss to clean between each and every tooth. With the correctly designed product, this between-teeth cleaning is both very simple and very effective. Dental floss may be used in place of, or along with, an interdental brush but is typically perceived to be more difficult. Flossers and floss handles may help in effective cleaning with floss.